What’s traceroute?
Traceroute is a command-line utility that returns details about the communication route between two nodes on an Web Protocol (IP) community. The utility sends out Consumer Datagram Protocol (UDP) check packets and tracks their path as they journey from the system the place the utility is working — the supply — to the vacation spot, which may be a server, router or different system on the community.
Directors and analysts can use traceroute as a diagnostic device to troubleshoot community and connectivity points. They’ll confirm which community path their information is touring and determine any locations the place there may be issues or uncommon routing patterns.
Traceroute is included with Unix and most Unix-like working techniques, together with Linux, macOS, FreeBSD and IBM AIX. If it is not included, customers sometimes can set up it manually, typically without spending a dime, utilizing a package deal supervisor equivalent to Yellowdog Updater, Modified or sudo apt.
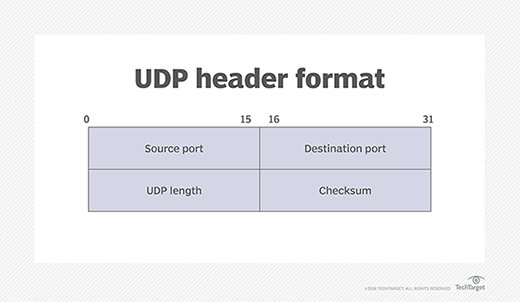
Although traceroute shouldn’t be included with Home windows techniques, Microsoft provides a comparable utility referred to as tracert. The tracert utility returns data just like what traceroute gives. The first distinction between the 2 is that traceroute transmits UDP packages by default, whereas tracert transmits Web Management Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets. Nonetheless, traceroute contains an choice for sending ICMP echo packets quite than UDP packets.
Traceroute is commonly in comparison with the ping utility, which will also be used to troubleshoot community points. However the two serve totally different functions. Ping can solely confirm connectivity between two community nodes; it gives no routing data. For that, a person wants traceroute or a comparable device.
How traceroute works
When two nodes talk throughout the web or a big non-public IP community, information packets journey — or hop — from one gateway to the subsequent till they attain their vacation spot. Traceroute gathers particulars about these gateways and generates an inventory that reveals the hostname and IP deal with of every one, if the data is offered. The utility additionally information the time it took, in milliseconds, for the UDP packet to journey round-trip between the supply laptop and the precise gateway.
If you run a traceroute command, the utility sends a packet with a time restrict of 1. This is called the time-to-live (TTL) worth, which signifies the variety of permitted hops. On this means, the restrict will probably be exceeded when it reaches the primary gateway that receives the package deal, inflicting the gateway to return a time exceeded message. Traceroute makes use of this message to find out the round-trip time for the information to journey between the supply laptop and the primary gateway.
After receiving the time exceeded message, traceroute will increase the TTL worth by 1 in order that will probably be exceeded when it’s acquired by the second gateway within the path quite than the primary. Upon receiving the packet, the second gateway returns its personal time exceeded message, which traceroute as soon as once more makes use of to find out the round-trip time. This course of continues for every hop within the path till the packet reaches its closing vacation spot or the request exceeds the whole variety of permitted hops.
Traceroute determines when a packet has reached its vacation spot by together with a port quantity that’s outdoors the traditional vary. When the vacation spot receives the packet, it returns a port unreachable message, which allows the utility to measure the time size of the ultimate hop.
Whereas a traceroute command is working, it shows details about every hop within the route path between the supply and vacation spot, itemizing the small print one hop at a time. By default, traceroute sends out three probes to every gateway after which shows the outcomes for every probe. The person can override the default variety of probes when working a traceroute command.
If details about the gateway shouldn’t be accessible for a particular probe, the utility will as an alternative show an asterisk. This may happen if the gateway fails to reply for any motive. For instance, it may be configured to ignore traceroute requests, or it may be too busy to answer such requests. If a hop is listed with three asterisks, it implies that all three probes failed to collect details about the gateway.
Working a traceroute command
To run a traceroute command, the person should specify, at a minimal, the utility’s title, traceroute, and the vacation spot’s hostname or IP deal with. For instance, the next command runs a traceroute request towards TechTarget’s website in Brazil.
traceroute www.techtarget.com.br
The next screenshot reveals the final 12 hops returned by this traceroute command, which originated on the U.S. West Coast. The trail contains locations in California and Brazil, with different doable areas in between.

The left-hand column lists the hop numbers. The primary hop proven is the 14th, and the final hop is the twenty fifth, which is the vacation spot. Every hop displays the three probes for that particular gateway. For instance, hop 23 reveals a gateway in Brazil. The gateway’s hostname is dist-fvcg2ita001.locaweb.com.br, and its IP deal with is 179.188.36.92. This data is adopted by the three round-trip instances, one for every probe.
In some instances, the hostname gives you a transparent sense of its location, as in hop 14, which signifies that the gateway is in Nice Oaks, Calif.
Hop listings typically present two or three IP addresses. This may happen for numerous causes, equivalent to excessive visitors volumes or energetic load-balancing operations. For instance, hop 22 signifies that the primary two probes went to at least one IP deal with and the third probe went to a second IP deal with. The instances related to every IP deal with point out the variety of probes to that deal with.
Some listings embrace solely the IP deal with and no hostname. You possibly can typically search for an deal with on a website equivalent to whatismyipaddress.com. This may be helpful in attempting to raised perceive how visitors is being routed throughout the web or the place roadblocks may exist. These websites will typically present particulars about who’s internet hosting a gateway and the place it’s positioned. If a list contains nothing however three asterisks, as in hop 19, you possibly can assume that the gateway didn’t reply to any of the probes. In that case, there may be little you possibly can be taught from this itemizing aside from {that a} hop was made.
Traceroute helps numerous choices for controlling the utility’s conduct and output. The precise choices rely on the underlying working system and its model of traceroute, though many choices are frequent throughout techniques. For instance, totally different variations generally help the -P choice, which helps you to specify an IP protocol equivalent to ICMP or Transmission Management Protocol, quite than utilizing the default UDP. One other frequent choice is -q. With this one, you possibly can specify the variety of probes per hop, thus overriding the default three.
See find out how to use traceroute to troubleshoot community issues.
