Latest analysis by cybersecurity firm ESET supplies particulars a couple of new assault marketing campaign concentrating on Android smartphone customers.
The cyberattack, primarily based on each a posh social engineering scheme and using a brand new Android malware, is able to stealing customers’ close to area communication information to withdraw money from NFC-enabled ATMs.
Fixed technical enhancements from the risk actor
As famous by ESET, the risk actor initially exploited progressive net app expertise, which permits the set up of an app from any web site outdoors of the Play Retailer. This expertise can be utilized with supported browsers resembling Chromium-based browsers on desktops or Firefox, Chrome, Edge, Opera, Safari, Orion, and Samsung Web Browser.
PWAs, accessed instantly by way of browsers, are versatile and don’t typically endure from compatibility issues. PWAs, as soon as put in on techniques, may be acknowledged by their icon, which shows an extra small browser icon.
Cybercriminals use PWAs to steer unsuspecting customers to full-screen phishing web sites to gather their credentials or bank card info.
The risk actor concerned on this marketing campaign switched from PWAs to WebAPKs, a extra superior sort of PWA. The distinction is refined: PWAs are apps constructed utilizing net applied sciences, whereas WebAPKs use a expertise to combine PWAs as native Android functions.
From the attacker perspective, utilizing WebAPKs is stealthier as a result of their icons not show a small browser icon.

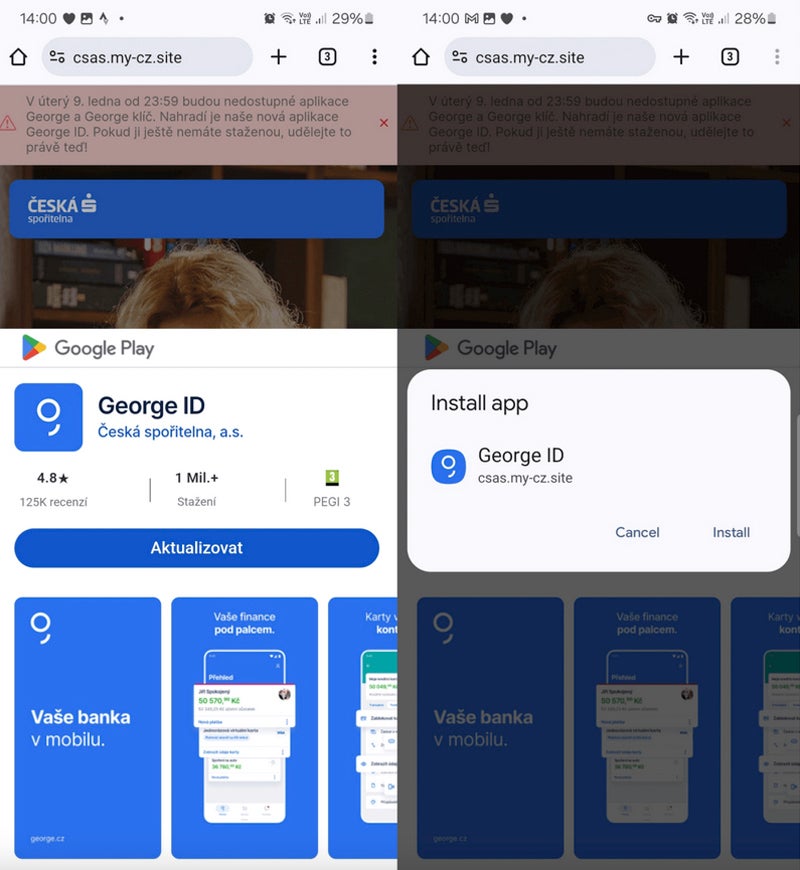
The sufferer downloads and installs a standalone app from a phishing web site. That individual doesn’t request any extra permission to put in the app from a third-party web site.
These fraudulent web sites typically mimic components of the Google Play Retailer to carry confusion and make the person consider the set up truly comes from the Play Retailer whereas it truly comes instantly from the fraudulent web site.
NGate malware
On March 6, the identical distribution domains used for the noticed PWAs and WebAPKs phishing campaigns all of the sudden began spreading a brand new malware referred to as NGate. As soon as put in and executed on the sufferer’s telephone, it opens a pretend web site asking for the person’s banking info, which is distributed to the risk actor.
But the malware additionally embedded a software referred to as NFCGate, a reliable software permitting the relaying of NFC information between two gadgets with out the necessity for the system to be rooted.
As soon as the person has offered banking info, that individual receives a request to activate the NFC function from their smartphone and to put their bank card in opposition to the again of their smartphone till the app efficiently acknowledges the cardboard.
Full social engineering
Whereas activating NFC for an app and having a fee card acknowledged could initially appear suspicious, the social engineering methods deployed by risk actors clarify the situation.
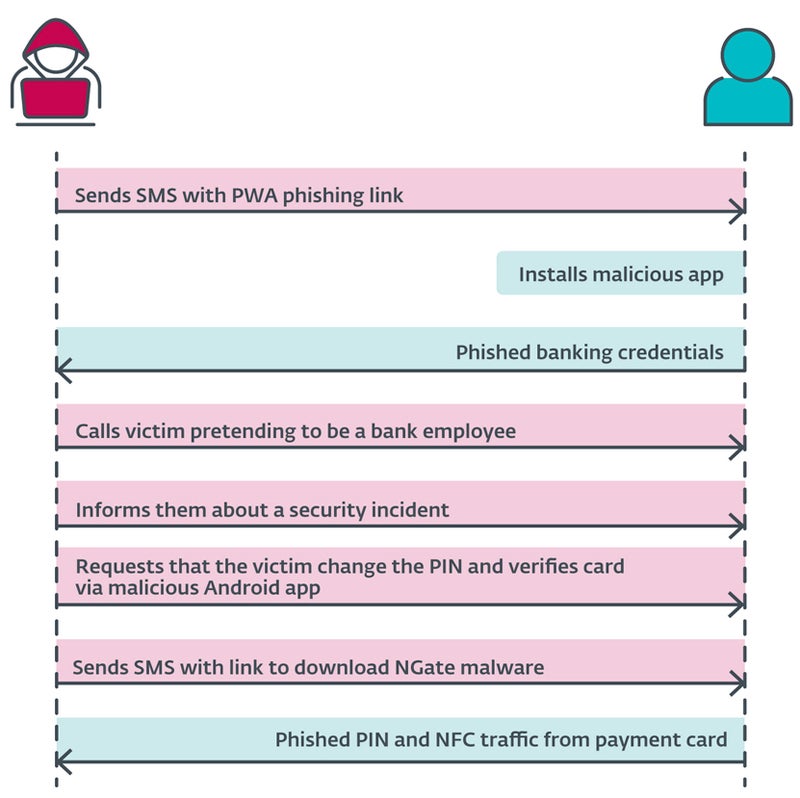
The cybercriminal sends a SMS message to the person, mentioning a tax return and together with a hyperlink to a phishing web site that impersonates banking corporations and results in a malicious PWA. As soon as put in and executed, the app requests banking credentials from the person.
At this level, the risk actor calls the person, impersonating the banking firm. The sufferer is knowledgeable that their account has been compromised, probably because of the earlier SMS. The person is then prompted to alter their PIN and confirm banking card particulars utilizing a cellular software to guard their banking account.
The person then receives a brand new SMS with a hyperlink to the NGate malware software.
As soon as put in, the app requests the activation of the NFC function and the popularity of the bank card by urgent it in opposition to the again of the smartphone. The information is distributed to the attacker in actual time.
Monetizing the stolen info
The knowledge stolen by the attacker permits for ordinary fraud: withdrawing funds from the banking account or utilizing bank card info to purchase items on-line.
Nevertheless, the NFC information stolen by the cyberattacker permits them to emulate the unique bank card and withdraw cash from ATMs that use NFC, representing a beforehand unreported assault vector.
Assault scope
The analysis from ESET revealed assaults within the Czech Republic, as solely banking corporations in that nation have been focused.
A 22-year previous suspect has been arrested in Prague. He was holding about €6,000 ($6,500 USD). In response to the Czech Police, that cash was the results of theft from the final three victims, suggesting that the risk actor stole rather more throughout this assault marketing campaign.
Nevertheless, as written by ESET researchers, “the potential for its enlargement into different areas or nations can’t be dominated out.”
Extra cybercriminals will probably use comparable methods within the close to future to steal cash by way of NFC, particularly as NFC turns into more and more standard for builders.
shield from this risk
To keep away from falling sufferer to this cyber marketing campaign, customers ought to:
- Confirm the supply of the functions they obtain and thoroughly study URLs to make sure their legitimacy.
- Keep away from downloading software program outdoors of official sources, such because the Google Play Retailer.
- Keep away from sharing their fee card PIN code. No banking firm will ever ask for this info.
- Use digital variations of the normal bodily playing cards, as these digital playing cards are saved securely on the system and may be protected by extra safety measures resembling biometric authentication.
- Set up safety software program on cellular gadgets to detect malware and undesirable functions on the telephone.
Customers must also deactivate NFC on smartphones when not used, which protects them from extra information theft. Attackers can learn card information via unattended purses, wallets, and backpacks in public locations. They will use the information for small contactless funds. Protecting circumstances can be used to create an environment friendly barrier to undesirable scans.
If any doubt ought to come up in case of a banking firm worker calling, cling up and name the same old banking firm contact, ideally by way of one other telephone.
Disclosure: I work for Development Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.
